How the Planning, Maintenance, and Timely Delivery of Refractory Materials Affect Production Reliability and Efficiency
In core industries whose production processes involve operations at extremely high temperatures—such as metallurgy, cement manufacturing, and related sectors—the timely delivery of refractory materials is an operational priority. In environments where every weld, shutdown, or kiln restart generates significant costs and delays, inadequate availability of these materials can result in serious production disruptions, additional financial burdens, and increased safety risks.
This text explores the role of modern information and logistics systems in optimizing risk management and enhancing supply chain reliability in this critical area.
Time as a Decisive Factor
Refractory materials are not commodities that can be added ad hoc. Their installation is strictly tied to planned maintenance periods, and any downtime—whether due to delivery delays or poor planning—directly threatens production continuity, safety, and budget control. In practice, producers often face unforeseen obstacles: inaccurate supplier forecasts, transportation delays, raw material shortages, or simply poor interdepartmental coordination.
Experience shows that even the best-laid plans cannot guarantee stability when global supply chains are disrupted. The COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, including wars and sanctions, have severely disrupted supply chains worldwide—including those in the refractory sector. In addition to objective obstacles, excessive optimism from some suppliers poses an added risk, as they often overpromise availability or performance in a bid to secure business, leaving customers in critical situations.
As a result, accuracy, reliability, and transparency across the supply chain are no longer luxuries—they are essential conditions for uninterrupted industrial production.
From Reactive to Proactive Supply Models
Traditional procurement models—such as ordering on demand or relying on local stock—are increasingly showing their weaknesses in today’s industrial environment. These approaches lack resilience to market volatility, consumption fluctuations, transport disruptions, or unexpected maintenance needs, often leading to shortages, overstocking, and inefficient cost management.
In response, more and more producers are adopting proactive, data-driven models for managing refractory materials. One successfully implemented example is the Kanban system, which RHI Magnesita deploys in cooperation with HTR Refractories. This system is based on daily monitoring of material consumption through direct warehouse outflow records. Using these data—alongside defined minimum and maximum stock levels, production lead times, logistics delays, material lifespan, and actual consumption dynamics—the system automatically triggers replenishment needs.
This ensures continuous material availability without overloading the warehouse, while optimizing budgets, as procurement and payment apply only to materials that are actually installed.
Implementing this system requires the involvement of multiple functional units: warehouse staff record material inflows and outflows, the technical team monitors material performance under real operating conditions, and the administrative team reconciles consumption, delivery, and production planning data. Thanks to this approach, the user is significantly relieved of logistics and inventory planning responsibilities and can fully focus on core production processes.
Digitalization as a Tool for Operational Safety
The adoption of modern information systems, digital tools, and optimized organizational models represents a crucial step in modernizing refractory material management. One successful example is the SAR+ system, which HTR Refractories promotes as “borderless integration.” This system enables:
- Centralized monitoring of stock levels and material flow across all users,
- Detailed consumption analysis by location,
- Precise delivery planning based on reliable and up-to-date data.
In practice, this results in efficient coordination between maintenance, warehouse, and administrative departments—all working toward the shared goal of ensuring that materials are always available where needed, while minimizing costs and avoiding downtime. In line with this approach, RHI Magnesita continues to develop and test digital solutions aimed at improving operational efficiency and safety.
However, digital transformation in heavy industry faces unique challenges. Sectors like metallurgy and cement often operate under conservative models, with firmly established procedures and resistance to change. Introducing digital solutions involves more than technical implementation—it requires a shift in organizational culture, redefinition of responsibilities, and additional employee training.
Aware of these challenges, HTR Refractories—as the official representative of RHI Magnesita on the local market—actively supports its partners throughout the entire digital transition process. Leveraging its own expert resources and operational experience, HTR not only implements the technology but also creates tangible added value—for both RHI Magnesita and end users. The ultimate goal is clear: to ease the transition to modern work models and enable partners to fully benefit from digital material management.
Yet, the real challenges are still ahead. The integration of artificial intelligence into core industries—including factories, mines, and facilities with high operational complexity—raises new concerns: from data security and ethical decision-making to the potential impact on the workforce. We still do not know how AI systems will integrate with existing production processes, or how industries operating under strict technical and safety standards will accept high levels of automation. Therefore, digital transition is not a one-off project—it is a long-term process that requires flexibility, vision, and a readiness for continuous adaptation.
In this context, HTR Refractories sees its role not only as a technology implementer, but also as a strategic partner—one that understands the specific demands of the industry and actively participates in building sustainable, adaptive, and secure digital ecosystems.
Partnership as the Foundation of Stability
From proactive supply models to digitized management systems, it is clear that success in modern industry depends not only on product quality, but also on the quality of collaboration. In that regard, HTR Refractories acts not only as a representative of global leader RHI Magnesita, but also as a local player with a clearly defined structure, well-developed logistical and technical capacities, and a deep understanding of the domestic market’s specific needs.
Our role goes beyond traditional distribution—we actively connect principal partners with end users and engage in every part of the value chain: from needs assessment and inventory planning, through technical support and consumption tracking, to education and joint development of new solutions. Together with our partners, we strive to ensure that materials are not only available but also used correctly and efficiently—in line with real working conditions and customers’ business goals.
Since our founding, our focus has never been on size, but on reliability. We build long-term partnerships based on transparency, expertise, and measurable results. This is a model that does not depend on market trends—it proves its value through stability, especially in times of uncertainty and pressure.
In an industrial environment where one hour of downtime can cause losses greater than the value of an entire product batch, the planning and logistics of refractory materials become just as critical as their chemical or mechanical properties. In this context, investing in smart systems, reliable processes, and qualified people is not a cost—it is a strategic decision.
Through its partnership with RHI Magnesita and its own network of knowledge and capabilities, HTR Refractories remains firmly committed to providing the domestic industry with what is now more important than ever: stability, expert support, and solutions that deliver results—not only in the current production cycle, but in the years to come.
Risto Ristovski
We are pleased to announce that HTR Refractories has become one of the signatories of the “Partnership for Equality” initiative, part of the important project “Promoting Equality in the Field of Work and Employment – Joint Initiative for Workplace Equality,” implemented by the Commissioner for the Protection of Equality with the support of the German Development Cooperation (GIZ).
The project aims to raise awareness and improve practices regarding equal opportunities in the labor market, encouraging employers to develop inclusive employment policies based on respect for human rights, diversity, and equality. It places particular emphasis on combating discrimination and promoting equal treatment of employees regardless of gender, ethnicity, age, health status, or any other personal characteristic.
As a socially responsible company operating in demanding industrial sectors, HTR Refractories has been committed from the beginning to creating a work environment where every employee has the opportunity to grow and contribute to their full potential. We believe that diversity among people is a source of strength, innovation, and success, and that inclusiveness is a necessary precondition for the sustainable development of modern companies.
Our goal is to build a workplace where everyone feels respected, accepted, and supported. We are proud to be part of an initiative that promotes these values.
By signing this initiative, we reaffirm our commitment to the principles of equality and fairness, and we invite all companies to follow a similar path in building a better and more just society.
🔗 You can learn more about the project and its objectives at the following links:
📽 YouTube video – “Diversity is Strength”
🌐 Official announcement from the Commissioner for the Protection of Equality
HTR Team
We are pleased to inform you that HTR Refractories has become the official and exclusive representative of SEMAO Solution SL from Spain for the Serbian market and the Southeast Europe region.
Through this strategic partnership, we are expanding our portfolio with high-quality solutions for oxyfuel cutting and spare parts for continuous casting processes, providing our partners in the steel industry with additional support in critical phases of production.
About SEMAO
SEMAO Solution SL, headquartered in Montblanc, Tarragona (Spain), specializes in the design, manufacturing, commissioning, and maintenance of oxyfuel cutting machines, as well as the production of spare parts for steel continuous casting systems. The company is composed of a team of engineers and technicians with over 20 years of industry experience. Their expertise and technical leadership have been implemented in dozens of renowned plants such as ArcelorMittal Gijón, Olaberria, Avilés, Hunedoara, Acerinox Europa, Tenaris Clarasi, Donalam Târgoviște, Megasider Zaragoza, and others.
SEMAO offers complete solutions for steel industry users, including:
– Spare parts and consumables for oxyfuel systems (nozzles, regulators, cutting torches, hoses, valves, motors),
– Maintenance and servicing of existing cutting machines,
– Design and implementation of new cutting systems,
– Technical support and consulting aimed at process optimization.
All products are manufactured in accordance with the highest European standards, with special emphasis on durability, precision, and operational safety.
Why is this important for the steel industry?
Oxyfuel cutting is a critical phase in steel processing, particularly for cutting ingots, blooms, slabs, and other semi-finished products.
Reliable equipment and the availability of spare parts directly impact:
– The productivity and safety of the production process,
– Reduction of downtime and maintenance costs,
– Longevity and precision of cutting operations.
This is why solutions like those offered by SEMAO are becoming essential elements of a stable and efficient steel production plant.
What does this partnership mean for HTR’s partners and customers?
With the addition of SEMAO solutions to our offering, HTR Refractories further strengthens its role as a strategic partner delivering top-tier technical solutions to the steel industry.
Our customers can now access:
– Premium equipment and spare parts for oxyfuel cutting,
– Fast and expert technical support,
– Access to cutting system design and modernization.
In this way, we enhance the entire value chain—from refractory materials and engineering to specialized cutting systems.
For more information, visit SEMAO’s official company presentation.
HTR Refractories Team
The role of refractory materials in incinerator operation is essential for efficient and environmentally responsible waste management. Incinerators, as key components in waste-to-energy plants, help reduce the volume of waste and generate energy. However, their operation can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, highlighting the need to improve the technologies and materials used in these processes.
The Role of Incinerators in Modern Society
Incinerators play a crucial role in reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, thereby cutting methane emissions—a potent greenhouse gas produced by decomposing waste. Additionally, the combustion of waste generates energy that can be used to produce electricity or heat, contributing to energy diversification and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Still, it’s important to note that incineration can produce significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other pollutants, which calls for careful management and the application of advanced emission control technologies.
The Role of Refractory Materials in Incinerators
Refractory materials are critical for lining the interior surfaces of incinerators, as they must withstand extreme temperatures and chemically aggressive environments during waste combustion. The quality and performance of these materials directly affect the efficiency, longevity, and safety of incinerator operations. Using high-quality refractories—such as those based on silicon carbide, magnesium, zirconia, and alumina—provides better resistance to wear and corrosion, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement.
How Refractory Materials Help Reduce the Carbon Footprint
Efficient refractory materials can contribute to lowering the carbon footprint of incinerators in several key ways:
- Improved energy efficiency: By using refractories with excellent insulating properties, heat loss is minimized, allowing for better use of generated energy and reducing the need for additional fuel.
- Emission reduction: Advanced refractory materials enable higher combustion temperatures, which can lead to more complete waste incineration and lower emissions of harmful gases.
- Durability and maintenance: Materials with greater resistance to wear and corrosion extend the service life of incinerators and reduce the frequency of overhauls, indirectly lowering emissions associated with the production and replacement of components.
Challenges and Perspectives
While incinerators offer a solution for reducing waste and producing energy, their role in the context of green energy and carbon footprint reduction remains a subject of debate. Some sources point out that CO₂ emissions from incinerators can be substantial and may hinder progress toward circular economy goals. Therefore, continuous work is needed to advance combustion technologies, improve refractory material performance, and implement carbon capture and storage systems to reduce their environmental impact.
In conclusion, refractory materials are vital for the efficient and eco-friendly operation of incinerators. Enhancing their properties directly supports carbon footprint reduction and improves the performance of waste-to-energy facilities—an essential contribution to the sustainable development of modern society.
When it comes to choosing the right refractory materials—those that can endure extreme conditions and deliver reliability at every step—the industry turns with confidence to the leader: RHI Magnesita. Their expertise and innovation set the benchmark in the refractory field, especially in the environment, energy, and chemical sectors. Learn more at: rhimagnesita.com – Environment, Energy & Chemistry
HTR Refractories Team
We are pleased to announce that as of March 2025, HTR Refractories has become the official sales agent for the Refliner™ brand in this region. Through this partnership, HTR Refractories further strengthens its offering of high-quality materials for the chimney systems and thermal insulation industry.
Refliner™, a brand of the renowned company RHI Magnesita, specializes in ceramic flue liners and high-quality fireclay materials. These products provide exceptional resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemical influences, and ensure long-lasting durability. Ceramic flue liners enable safe and efficient exhaust gas evacuation, while fireclay materials allow optimal heat storage and gradual heat release, making them ideal for fireplaces, stoves, and industrial applications.
As the general representative of RHI Magnesita, we also introduce the Refliner brand for chimney pipes in the markets of Serbia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Albania.
This strategic partnership brings multiple benefits:
✅ A broader range of premium products for customers in the region.
✅ Enhanced technical support and availability of Refliner materials.
✅ Strengthened HTR Refractories’ position in the building materials market.
With this move, HTR Refractories not only reaffirms its commitment to providing high-quality solutions in the industry but also opens new opportunities for growth and development in the construction and industrial materials market.
For more information about our products and collaboration opportunities, feel free to contact us through our official channels.
We share an article from the latest RHIM Bulletin.
Abstract
Optimum management of steel ladles plays a crucial role for efficient and sustainable steel production. Regarding ladle wear linings, steelmakers typically have two main approaches. The most common is a fully bricked lining, offering advantages such as slag and high-temperature resistance, along with reliable campaign lifetimes. An alternative, which has demonstrated many benefits in recent years, is monolithic technology based on alumina spinel. However, whichever lining concept is used, performance can be further improved with intermediate repairs of high-wear areas using shotcrete. This article presents results collected over multiple years at different steelworks, all of which benefited from this type of repair method. For example, savings in the quantity of refractories used were observed, as well as reductions in waste and CO2 emissions.
Introduction
Over many years, ample proof has accumulated that zoning different areas of the steel ladle with specific refractory materials is the most effective and safe approach to optimise service life. Currently, steelmakers generally rely on one of two concepts for the ladle refractory wear lining. While the majority trust bricks, which provide good high-temperature resistance, excellent slag protection, easy heat up, and reliable service life, others have already switched to monolithic solutions based on alumina spinel, with high thermal stability, good hot strength, excellent resistance to thermal spalling, as well as low carbon pickup and decreased thermal conductivity, which are important for the production of ultra low carbon steels and energy saving, respectively. However, since both concepts see uneven refractory wear in different zones, repair of these regions with sprayable materials has emerged as a solution to increase the number of heats before complete relining is required.
Comparison of Two Standard Lining Concepts
Steel ladles play a critical role in steel production, serving as vessels for transporting and refining steel through various stages of secondary metallurgy. The refractory lining of these ladles is subjected to chemical, thermal, and mechanical wear. For these reasons, it is essential to carefully select the type of refractories, installation technique, and maintenance to provide as long a service life as possible. Due to the wide-ranging requirements, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Steel shop managers need to balance different parameters, such as durability, balanced performance, low consumption, resistance to slag attack, safety, ease of installation, quick heating up, capacity optimisation, insulation properties, flexibility, and cost effectiveness. Finding the best compromise among these complex requirements is a continuous challenge. While MgO-C bricks have long been favoured for the ladle wear lining, due to their high-temperature resistance and reliable service life, the steel industry is increasingly recognising the potential of alumina spinel monolithic refractories. For example, research conducted over two decades ago revealed that these monolithic products not only compete with traditional lining materials, but also offer additional benefits, such as increased ladle capacity and reduced thermal losses [1].
Recent reports and articles have further supported these findings, highlighting the advantages of alumina spinel monolithic refractories [2–5]. Lower operating costs and improved consistency in the steel carbon content, make these refractories appealing to steelmakers seeking enhanced efficiency and higher quality steel production. Furthermore, transitioning from MgO-C bricks to alumina spinel monolithic refractories can contribute to a reduction in CO2 emissions, both during refractory production and operation, making them an environmentally sustainable choice. Another advantage of monolithic refractories is their ability to minimise waste generation by enabling targeted repairs instead of complete demolition and relining, thereby optimising resource utilisation in the steelmaking process.
Introduction to Cyclic Shotcrete Repair
A previous article presented at the 63rd International Colloquium on Refractories showcased an innovative cyclic shotcrete repair technique for steel ladle management [6]. The following summary provides an overview of the repair cycle and calculations for long-term analysis after multiple years in use. Cyclic shotcrete repair involves applying protective layers of monolithic castable onto an existing brick lining in a repetitive manner. By combining the advantages of monolithic and brick linings, this method offers a flexible and reliable solution for ladle lining repair.
The shotcrete technique, known for its flexibility and ability to create refractory linings with similar technical features as traditional casting methods, is utilised in this application. A castable mix is sprayed at high pressure onto the surface, where it rapidly sets, allowing for targeted repairs without complete demolition and relining. A comparison between the typical brick lining cycle and the cycle with shotcrete repair reveals the advantages of shotcrete application (Table I). Without steel zone repair, the slag line can only be replaced once before complete relining becomes necessary. However, with shotcrete repair in the steel zone, the slag line can be changed multiple times before complete relining is required.
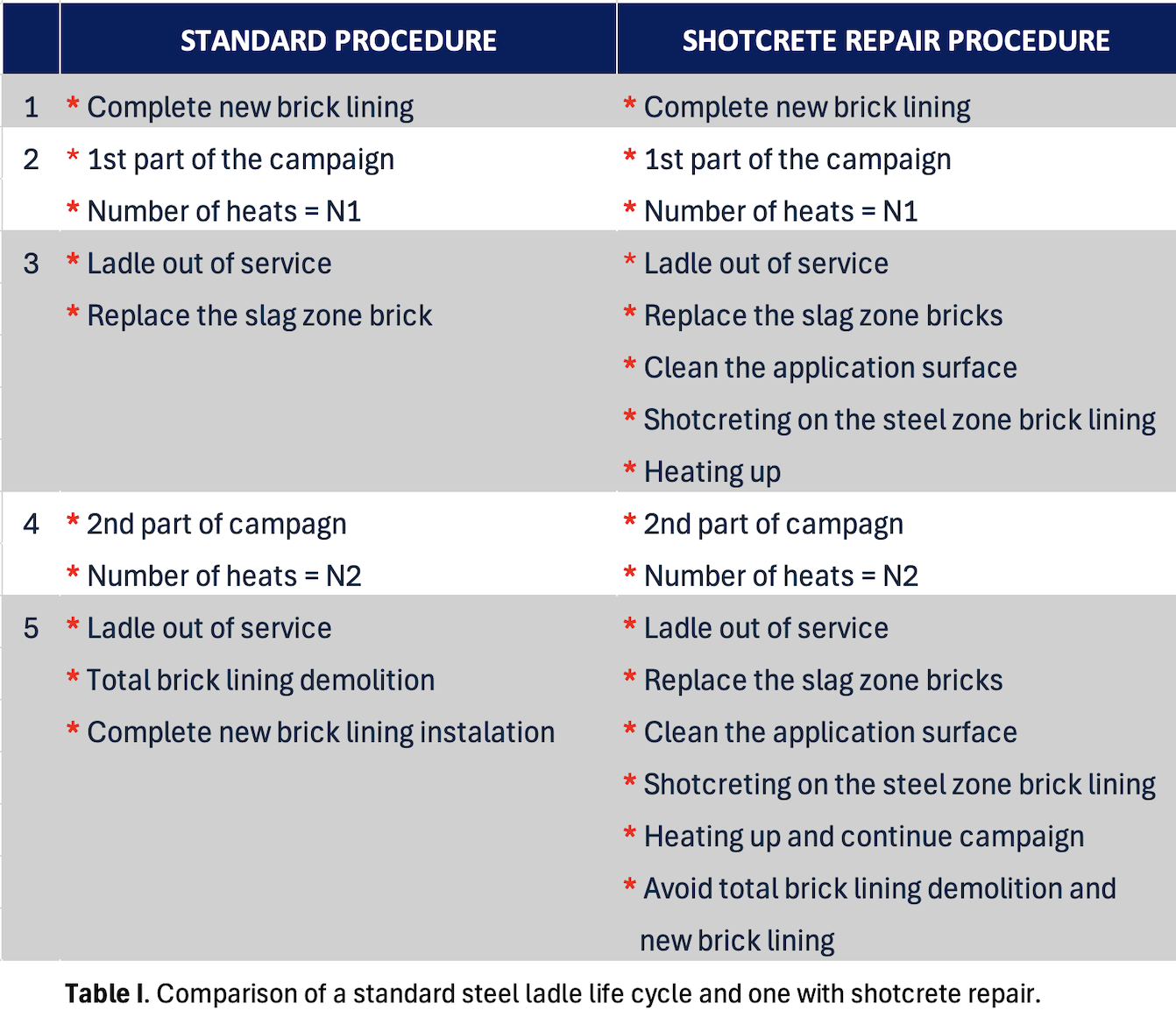
The shotcrete application extends the ladle campaign life, reduces specific consumption and costs, while maintaining the use of traditional brick linings. Specifically, wear occurs to the shotcrete layer, while the original bricks remain intact. This technology offers significant benefits, including prolonged ladle campaign life, easy visual wear control, and reduced refractory lining waste. As a result, it leads to substantial reductions in specific refractory consumption and operational costs without compromising the ladle availability, reliability, and safety.
Analysis of Long-Term Cyclic Shotcrete Repair
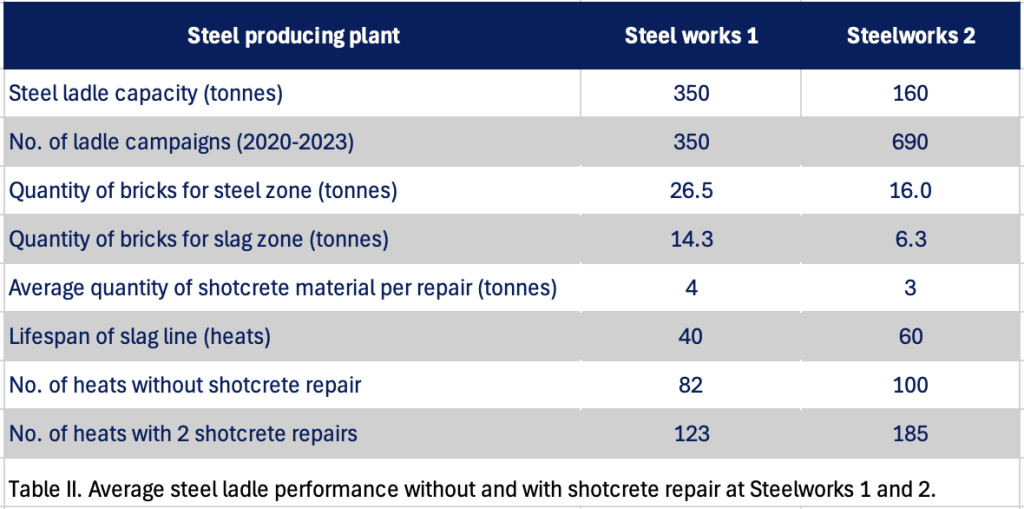
Shotcrete repair is a standard maintenance solution, applied in numerous steelworks (Figure 1). The increased number of ladles repaired in this way has led to optimised cleaning techniques, installation, and heating curves, resulting in more reliable ladle management. This section presents long-term cyclic shotcrete repair results obtained from two steelworks. On average, the slag line bricks at Steelworks 1 were replaced after approximately 40 heats. The ladle then continued to operate for another 40 heats. However, at around 82 heats, the bricks in the steel zone became too worn to complete another slag zone cycle, resulting in the complete demolition of the ladle. In the new campaign life cycle, the introduction of two shotcrete repairs in the steel zone and two slag zone brick replacements has extended the ladle’s campaign life by 50% (Table II).
Analysis of Long-Term Cyclic Shotcrete Repair
Shotcrete repair is a standard maintenance solution, applied in numerous steelworks (Figure 1). The increased number of ladles repaired in this way has led to optimised cleaning techniques, installation, and heating curves, resulting in more reliable ladle management. This section presents long-term cyclic shotcrete repair results obtained from two steelworks. On average, the slag line bricks at Steelworks 1 were replaced after approximately 40 heats. The ladle then continued to operate for another 40 heats. However, at around 82 heats, the bricks in the steel zone became too worn to complete another slag zone cycle, resulting in the complete demolition of the ladle. In the new campaign life cycle, the introduction of two shotcrete repairs in the steel zone and two slag zone brick replacements has extended the ladle’s campaign life by 50% (Table II).

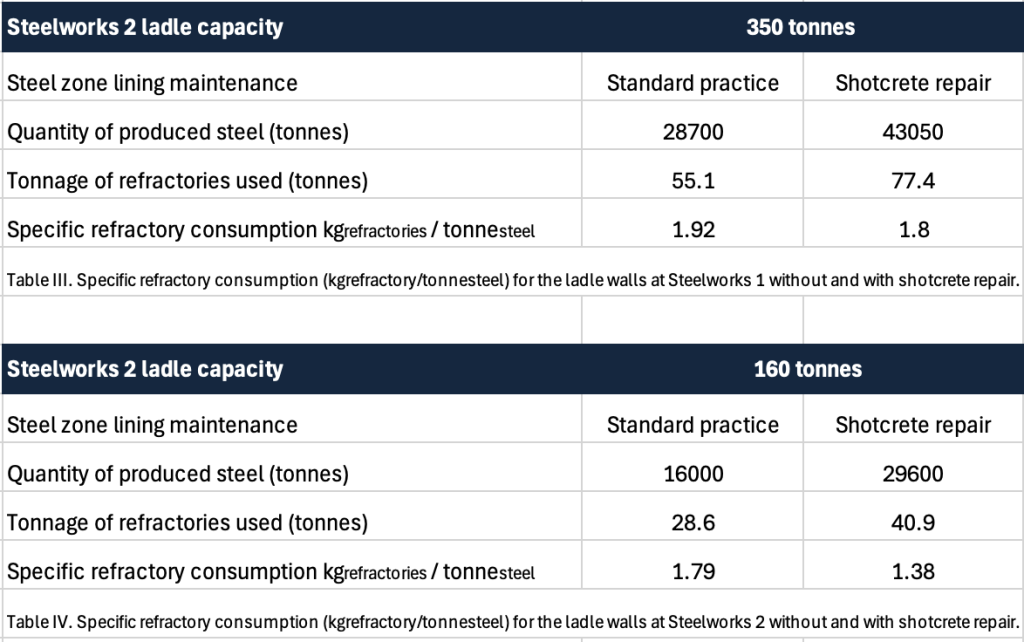
Using the annual steel production figure of 3.5 million tonnes at Steelworks 2, the number of ladle wear linings required per year was calculated. This enabled the annual amount of refractories needed for the steel ladle wall to be estimated for the standard practice and with shotcrete repair, and from this figure the amount of refractory waste, considering the ladle is demolished when the bricks reach 30% of their original thickness. These numbers reflect significant savings in refractory costs, increased steel ladle availability, reduced refractory waste, and lower CO2 equivalent (CO2e) emissions coming from refractory production when shotcrete repair is used. The latter was calculated assuming average cradle-to-gate product carbon footprints [7] of 2.472 and 1.344 tonne CO2e/tonnerefractory for the bricks and monolithic, respectively (Table V and VI).
New Installation Method—SHOTGUN
Shotcreting is a versatile monolithic application technique where a castable mix is sprayed onto a surface at high pressure, rapidly setting in place. It offers exceptional flexibility, allowing it to be used in various locations regardless of complex geometries. Crucially, shotcreting achieves refractory linings with comparable technical features to traditional vibrating casting methods, particularly in terms of mechanical parameters. However, shotcrete is typically not used for small repairs due to the higher equipment cost, longer preparation time, and increased cleaning requirements after installation. These limitations are easily overcome by larger steelworks where the number of steel ladles and the quantity of installed material are high, and top-of-the-line performance is expected. On the other hand, for smaller steel mills, these limitations can be a dealbreaker, hindering them from modernising their steel ladle management. To assist them in moving into the greener future, a new installation technique and material that enables utilisation of gunning machines to apply similarly performing material as shotcrete have been developed. A schematic of this SHOTGUN system, which includes a modified gunning machine, high-pressure water pump, compressed air source, accelerator pump, and a special SHOTGUN nozzle (Figure 2), is depicted in Figure 3 [8].
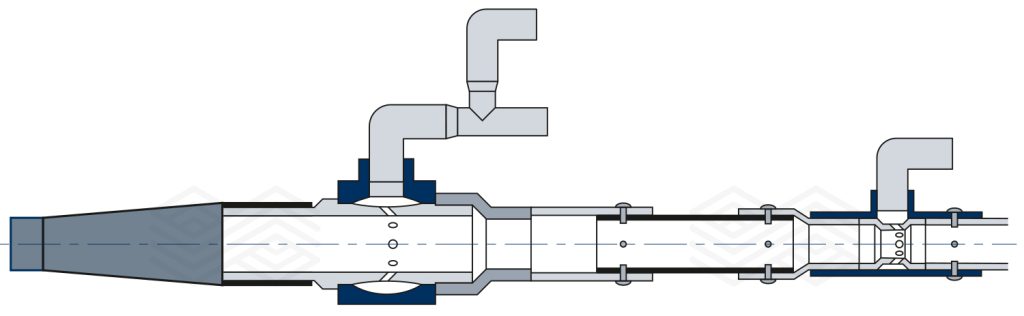
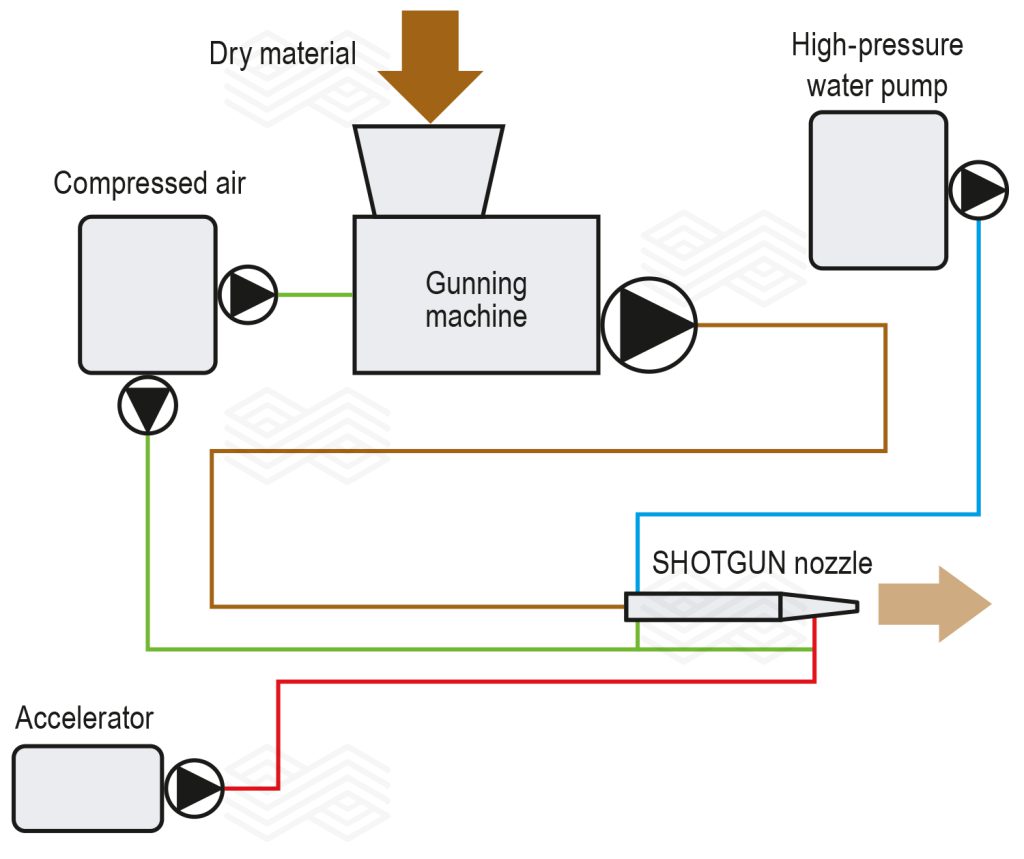
This system eliminates the need for a planetary mixer and shotcrete pump, which take up a lot of space and are costly, while also significantly reducing setup time and manpower. Since water is added at the nozzle, there is no need to clean the pipes, and no material is wasted that would normally remain in the mixer, pump, and pipes. As the existing shotcrete material (e.g., SEVEN SHOT 92 NR 08 Z) was not fully compatible with the new installation system, which requires a material that is dry pumpable without separation and can be wetted out in a short amount of time, the particle size distribution and additives were modified, giving rise to a new family of SEVEN SHOTGUN products.
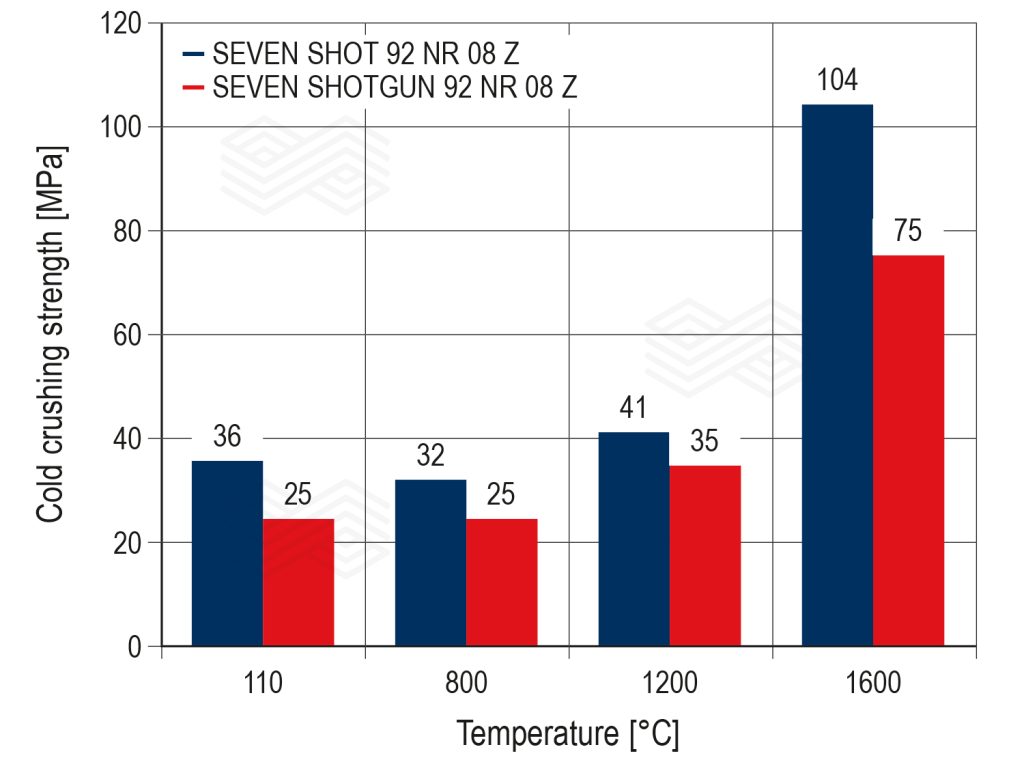
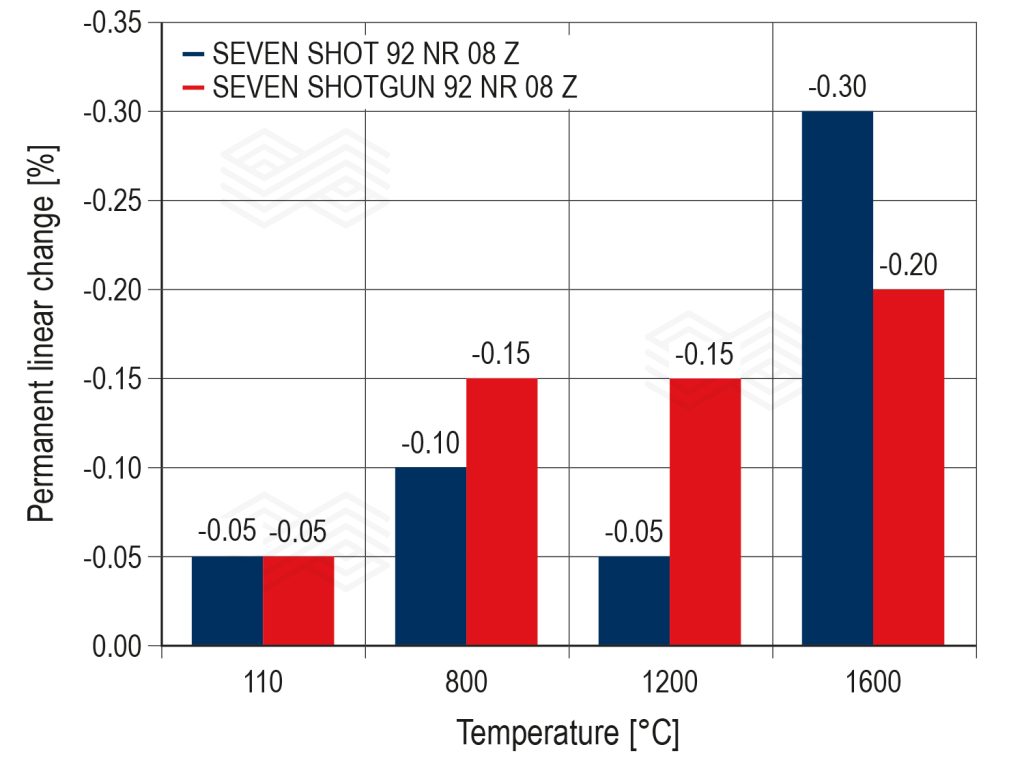
A comparison of the SEVEN SHOT 92 NR 08 Z and SEVEN SHOTGUN 92 NR 08 Z physical properties shows that both have high cold crushing strength (CCS) values, especially at operating temperatures (Figure 4). Furthermore, the permanent linear change (PLC) is relatively constant for both products and far from the critical value of -1.5% (Figure 5). Although SEVEN SHOTGUN 92 NR 08 Z has slightly lower CCSs, the values are still sufficiently high, and the less negative PLC reduces the stress experienced by the material.
Industrial Trials of SHOTGUN at Steelworks 3
At Steelworks 3, a bottleneck during the standard campaign was wear in the ladle steel zone lining. The application of SEVEN SHOTGUN 92 NR 08 Z during replacement of the slag zone bricks extended the campaign until the bottom and slag zones became limiting factors for the steel ladle’s life cycle. This has been confirmed in several steel ladle campaigns. With this solution, all zones reach their end of life at the same time, which is a crucial parameter in economical calculations for all refractory linings and significantly reduces the amount of wasted material.
Conclusion
Shotcrete repair has proven to be an effective solution to improve steel ladle performance. These repairs extend the ladle service life, reduce waste, and decrease refractory consumption per tonne of steel. As a result, operating costs are lowered, and the environmental impact is reduced. Furthermore, the repair process helps equalise the life cycles of different zones within the ladles, resulting in further refractory waste reductions.
The introduction of the new SHOTGUN solution has made these benefits more accessible and easier to implement. Laboratory tests have shown only minimal reductions in physical values of the SEVEN SHOTGUN 92 NR 08 Z compared to the standard shotcrete material, ensuring high quality repairs and the feedback from initial field trials has been positive. It is expected that this solution will be particularly useful for smaller steel mills seeking to optimise their steel ladle performance. RHI Magnesita is confident that further industrial trials will establish SHOTGUN as a reliable installation technique, enabling steel producers to transition towards a greener and more efficient future.
References
[1] Buhr, A. Refractories for Steel Secondary Metallurgy. CN-Refractories. 1999, 6(3), 19–30.
[2] Vatanen, J. Monolithic Ladle Lining in a 3-Converter-Shop. Presented at Steel Academy’s 12th International Seminar on Refractory Technology: Steel Ladle Lining, Concepts for a Complex Reactor. Bonn, Germany, September 14–16, 2022.
[3] Siebring, R. Economics in Refractory Usage. Presented at Steel Academy’s 12th International Seminar on Refractory Technology: Steel Ladle Lining, Concepts for a Complex Reactor. Bonn, Germany, September 14–16, 2022.
[4] Buhr, A. Trends in Clean Steel Technology and Steel Ladle Lining. Presented at Steel Academy’s 12th International Seminar on Refractory Technology: Steel Ladle Lining, Concepts for a Complex Reactor. Bonn, Germany, September 14–16, 2022.
[5] Akselrod, L.M. and Garten, V. An Alternative Lining of Steel Ladles: Technical and Economic Aspects. Ferrous Metallurgy Bulletin of Scientific Technical and Economic Information. 2018, 12, 72–80.
[6] Copetti, G. and Folco, L. Steel Ladle Management: An Integrated View of the Challenges in Resistance, Environmental Impact, and Economic Issues. Presented at 63rd International Colloquium on Refractories (ICR 2020). Aachen, Germany, September 16–17, 2020.
[7] Joos-Bloch, M., Rechberger, L., Haider, C., Moulin-Silva, W., Wucher, J. and Drnek, T. Product Carbon Footprint of Refractory Products. Bulletin. 2023, 39–44.
[8] European patent EP 3 858 491 A1. International publication number WO 2020/040665
Authors
Luca Folco
RHI Magnesita, Divaca, Slovenia
Alan Kranjc
RHI Magnesita, Divaca, Slovenia
Source: RHI Magnesita
In today’s world, sustainability is not just a moral responsibility but a crucial business necessity, particularly in Europe. Companies are increasingly required to adapt to evolving environmental policies and incorporate sustainable practices into their operations. This shift is driven by various factors, including regulatory requirements, market competition, environmental accountability, reputational concerns, and the pursuit of innovation and profitability.
The European Union has set ambitious goals under the European Green Deal to achieve climate neutrality by 2050. This includes stringent carbon emission standards and mandatory environmental compliance for businesses. Regulations such as the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the Climate Law enforce the integration of sustainability into corporate strategies, compelling organizations to report on their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. Moreover, policies favoring circular economy principles promote recycling, waste reduction, and the use of renewable resources, requiring companies to reevaluate and modify their business practices.
Market dynamics also play a critical role in this transition. Consumers increasingly favor eco-friendly products and services, while investors prioritize companies with robust ESG credentials. Multinational corporations demand their suppliers adhere to environmental standards, driving sustainability across value chains. These market pressures highlight the necessity for businesses to align with sustainable practices to maintain competitiveness and attract investment.
Environmental responsibility is another key driver. Industries are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, necessitating sustainable practices to mitigate climate change and conserve natural resources. Unsustainable practices, such as resource overexploitation or environmental pollution, are increasingly scrutinized by the public, further emphasizing the need for corporate accountability.
Beyond environmental and market imperatives, companies committed to sustainability enhance their reputations and build trust with consumers and employees. Such organizations are better equipped to avoid penalties, protests, and boycotts while positioning themselves as market leaders. Sustainability efforts also foster innovation, leading to resource efficiency, reduced waste, and the development of new products, technologies, and business models that open new markets and drive profitability.
Leaders in Sustainability: HTR Refractories brings leader producers in the local market
HTR Refractories has the privilege of representing global leaders in sustainability, such as RHI Magnesita and Estanda, on the local market. These companies exemplify how integrating sustainable practices into business operations leads to innovation, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced value for stakeholders.
RHI Magnesita, a global leader in refractory materials, has adopted a comprehensive sustainability strategy. The company aims to reduce its CO₂ emissions intensity by 15% by 2025 compared to 2018 levels. This goal is supported by initiatives such as increased use of recycled materials, improved energy efficiency, and a shift toward low-carbon energy sources. By 2025, RHI Magnesita plans for 15% of its raw materials to come from recycled sources, promoting a circular economy while significantly reducing carbon emissions. Their innovative “4PRO” contract model, introduced in November 2024, revolutionizes refractory solutions for high-temperature industries such as steel, cement, and glass, advancing both technological and sustainability goals. RHI Magnesita’s achievements are reflected in its high ESG ratings and adherence to international standards such as ISO 14001, ISO 50001, and ISO 45001.
Estanda, a Spanish manufacturer specializing in high-quality steel castings, demonstrates how sustainability can be integrated into industrial processes. By using 100% recycled steel scrap, the company minimizes waste and enhances resource efficiency. All production processes rely on renewable energy, significantly reducing their environmental footprint. Estanda also exemplifies circular economy principles by recycling sand used in mold-making and effectively managing waste. In 2023, the company’s CO₂ emissions were limited to just 208.2 kg per 1,000 kg of cast steel, a testament to its environmental stewardship. Additionally, Estanda supports sustainable supply chains by providing clients with detailed CO₂ assessments, enabling better environmental management.
Driving Local Impact Through Sustainability
HTR Refractories is dedicated to leveraging the expertise of RHI Magnesita and Estanda to foster local innovation and sustainability. By introducing these global leaders’ products to the market, HTR Refractories supports local manufacturers in developing new products, optimizing production processes, and aligning with sustainability standards. This collaboration not only enhances the value of final products but also contributes to the broader transition toward a sustainable economy.
In conclusion, the integration of sustainability into business practices is no longer optional. Companies that embrace this transformation position themselves as leaders, not just in their industries but also in the global effort to create a sustainable future. Through its partnerships, HTR Refractories demonstrates how businesses can achieve innovation, profitability, and environmental stewardship, setting an example for the entire industrial sector.
HTR Refractories
Photo: iStock
A commentary by Stefan Borgas, CEO, RHI Magnesita
This year has been dubbed “the year of elections”. By the end of 2024, 64 countries will have or have had new governments or administrations including the EU, US, Japan, UK, France and India. Businesses worldwide are anticipating what the possible policy changes will be and will mean for them. Especially critical industries could become crucial for an economic recovery.
The world has changed
To fully understand the challenges, we must recognize the geo-political disruptions have changed the world. From our global perspective at RHI Magnesita we clearly see that a series of shocks – including the pandemic, regional wars, the rise of protectionism measures on climate change and immigration – have collectively battered long-established supply chains and global trade networks. The industrial sector, especially heavy and basic industry in most global economies has been in stagnation for more than two years; a recovery is not at sight. Service and IT sectors cannot in the long-term balance out the industrial stagnation or even downturn. A prolonged, much more uncertain environment is testing the way we plan and manage global businesses. The global economy of the past 40 years is no more; industries must be prepared to find new answers and solutions.
The mission-critical refractories industry is feeling this seismic shift keenly. Alarm bells should ring with policymakers and industry leaders around the world, if this industry were to suffer materially.
Refractories are highly engineered materials designed to withstand very high temperatures well in excess of 1,200° C. They coat the inside of blast furnaces, crucibles and kilns which produce steel, aluminium, cement, glass, chemicals and many other materials that make-up the building blocks of modern societies. They are a very small part of the cost base but completely essential to the industrials sector which is the backbone of economic growth.
The continuing demand downturn and its impact
Another year that started with hopefulness for the refractory industry has taken a turn in recent months. Continuing poor macro-economic conditions, new economic policy measures and trade barriers have resulted in a market downturn in almost every geography due to the downturn of user industries. Even regions such as India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East, which we had anticipated to be “bright spots”, have also shown signs of short-term demand weakness.
Western economies are experiencing an industrial recession due to shrinking demand from the construction, transport and machinery sectors. The structural reduction of the industrial sector in China, the largest consumer and producer of metals, glass and cement, has led to an imbalance in world trade. The country is going through a deep structural shift from a supply-driven economy to a demand driven economy – this is painful, it will take time, and it will cost a lot of money, patience and adjusting – for the Chinese as well as for the entire world. Low domestic consumption has accelerated Chinese steel, metals, glass, and refractory exports, which cannot be easily absorbed due to low demand in destination economies.
Some analysts and commentators do not forecast any improvement in the demand situation for at least the next 12-18 months. This would then result in more than three years of continued downturn or industrial recession. Others are even beginning to question whether demand will ever return to prior levels.
The global demand downturn is further complicated by the recent increase in sea freight costs, transit times and reduced freight reliability arising from the Red Sea crisis, low water levels in the Panama Canal and port congestions. Rising bauxite and alumina prices due to a supply shortage for example, have resulted in cost inflations of alumina-based products, to reflect the higher cost of raw materials. The same is about to happen in magnesite based raw materials too. Developed markets continue to face the incremental challenge of labor cost inflation which is still not being absorbed.
With raw materials making up ca. 70% of total cost of goods, we must pass these inflationary cost increases on to our customers to reasonably protect our already thin margins. Industry-wide, capital expenditure and innovation efforts are already at a dangerous minimum.
The repercussions of a widespread closure of unprofitable refractories plants or production lines could be severe. If, and when, the turning point for an economic recovery comes, world leaders will be bitterly disappointed if steelmakers are hamstrung by shrunken refractories supply capability. So, one would assume that the issues impacting the future of the refractories industry would be high on policymakers’ agendas. Yet still, the refractories industry – the essential ingredient for making our cars, houses, plastics, even paper – does not have the public attention it justifies.
In Europe, Ursula von der Leyen’s new EU Commission announced in September signaled a commitment to reinvigorate Europe’s industrial strategy, but this will be futile if the needs of the refractories industry aren’t taken into account.
For example, RHI Magnesita is calling for a review of the Critical Raw Materials Act to include high-purity magnesia and dolomite, two key refractories precursor minerals, to ensure that refractories production in Europe remains financially viable and innovation continues.
The refractory overcapacity
But as politicians change and policies get modified, I also encourage our industry to help itself:
We today have a self-inflicted overcapacity problem which must no longer go unaddressed. A number of major producers have been progressively building out new greenfield plants in a flat, no-growth industry with pricing challenges. We estimate that excess capacity is running at some 40% above demand and, shockingly, growing. For example, India alone is seeing an addition of almost 300 kt of new greenfield capacity in the next 2-3 years. Reasonable growth of customer demand in India has led to a frensy race for new capacities by many refractory players in India jointly producing very large overcapacity. How rational is this in the context of the macro challenges outside of our industry’s control? RHI Magnesita has been pursuing growth via an M&A strategy while focusing on bringing new innovations and greener production methods to the industry.
Decarbonization needs policy support
Value-add instead of old-style mass production must become a priority. Innovations including refractories recycling or refractory life extension through digital data usage must become more widespread to improve the sustainability of our product and help our customers improve theirs. The opportunity if we focus on innovation is still there.
The Governments and policy makers can help here as well. Within RHI Magnesita’s own sustainability agenda we have ambitions to take a lead on hydrogen adoption and carbon capture and utilization – neither of which will be possible without policy intervention to support new technologies, risk capital to allow first-mover industrial installations, as well as new infrastructure that will benefit a wider industrial decarbonization journey and help the industrial sector to grow again.
Refractories are an overlooked ‘critical’ global industry, a facilitator of the building blocks of modern society. Today, macro crises have led us to a highly challenging juncture. It is essential that we adapt quickly to help power a global economic recovery, and for this we need horizontal and vertical private sector collaboration and public sector recognition, support and engagement.
Source: RHI Magnesita
RHI Magnesita’s Low CO2 Gunning Mixes
RHI Magnesita has been developing sustainable refractory solutions, focusing on gunning mixes that incorporate circular raw materials to reduce the carbon footprint. Our efforts have resulted in gunning mixes with a 30 -85% reduced carbon footprint in EU, CIS, and Türkiye, reducing customers’ Scope 3 CO2 emissions. This initiative is part of a broader commitment to sustainability and environmental stewardship in the refractory industry.
About the ANKERJETY- Series
RHI Magnesita’s ANKERJET Y line, a well-established brand in sustainable gunning mixes, is based on MgO-C circular raw materials. Currently, the brand is produced in Veitsch and is mainly available for the European market. The portfolio includes eight distinct product variations, specifically designed for use in EAF, BOF, and steel ladles, ensuring optimal performance.
ANKERJET YW12-AT stands out as an innovative recycling solution that replaces traditional sintered magnesia formulations with a cutting-edge circular MgO-C concept. It is designed for the hot repair of ladle linings through direct gunning, which has proven to be one of the most effective methods for extending ladle lifespan. The ANKERJET YW12-AT gunning mix incorporates up to 30% circular raw material, successfully displacing traditional brands without any loss of performance.
From Development to Successful Implementation
RHI Magnesita has successfully introduced the innovative ANKERJET YW12-AT brand at a key customer site in Southern Europe, marking a significant advancement in sustainable refractory management. This initiative is part of our commitment to circular economy practices, as RHI Magnesita manages total refractory solutions.
In a groundbreaking test conducted with 100-ton ladles, the product demonstrated excellent adhesion, minimal rebounding, and superior heat management capabilities—performance that met and exceeded expectations.
Over five days, a dedicated team conducted extensive testing, applying 24 tons of the material across 12 ladles and 21 different application samples. The results were compelling, with operators reporting that ANKERJET YW12-AT adheres better than conventional products, even under more challenging conditions in the slag line of the ladle.
The positive outcomes have prompted the steel plant managers to authorize a transition in their product portfolio. Beginning June 2024, ANKERJET YW12-AT has started to replace traditional products as the standard offering, allowing for the substitution of 900 tons of conventional material with a circular solution. This shift is projected to prevent approximately 500 tons of CO2 emissions annually, equivalent to 12 turns by truck around the world!
By adopting ANKERJET YW12-AT, customers can reduce their CO2 emissions by up to 30% per ton of installed material compared to virgin brands. This innovative solution represents a transformative step in the market.
If you are interested in knowing more about RHI Magnesita’s sustainable gunning mixes, please visit Sustainable Refractory Solutions—New Gunning Mixes Containing Circular Material | RHI Magnesita.
For more information about the evolution of ANKERJET YW12-AT or similar products available in your region, please do not hesitate to us.
Source: RHI Magnesita
In a rapidly evolving world, adaptation is no longer optional—it is essential. RHI Magnesita is driven by a profound purpose: to master heat and enable global industries to construct a sustainable modern life.
RHI Magnesita aims to transcend the traditional role of selling refractory products and basic services with advancements that necessitate a more holistic approach.
4PRO Business Model addresses the dynamic challenges faced by industries and society today and emphasizes four key pillars: Performance, Partnership, People, and Planet. Through this, the companygoes far beyond selling refractory products and basic services: the portfolio now includes recycled products, robotics, systems, sensors, digital solutions, decarbonization solutions, and green steel solutions. 4PRO emphasizes transparency, operational safety, and social responsibility while supporting a circular economy and helping industries transition to greener practices. More than a contract, it is a new form of interaction with customers and an innovative solution to the contemporary challenges of the industry and society.
For more details, visit 4PRO by RHI Magnesita.
Contact
Contact us
If you are interested in cooperating, feel free to contact us.
Our friendly team is at your disposal. You can contact us by e-mail.